Related physics: Antimatter, Antiproton
Related equipment: AD
Experimental Cycle
Experimental Cycle
ALPHA is not just one apparatus. The apparatus consists of different sub-elements, which are all produced and maintained by experts from around the world. At CERN we then rebuild these components and make the whole experiment work together.
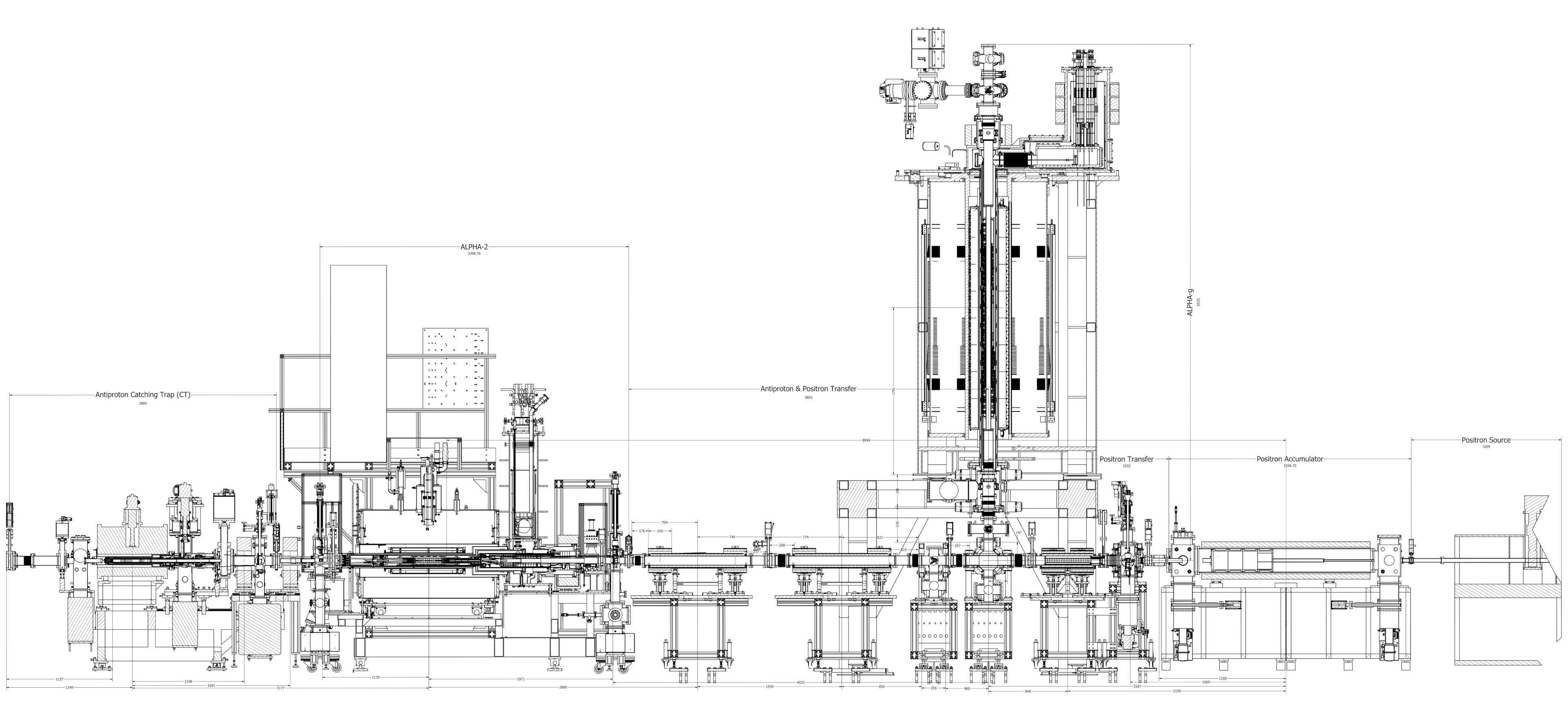
-
1. Get Antiprotons
-
2. Get positrons
Related physics: Antimatter, Positron
Related equipment: Sodium source, Positron accumulator -
3. Catch antiprotons
Related physics: Penning Trap
Related equipment: Catching Trap, Penning Trap -
4. Cool and compress antiprotons
(with electrons)
Related physics: Plasma physics, electron cooling, rotating wall, evaporative cooling, SDREVC (rotating wall with evaporative cooling)
Related equipment: Penning Trap -
5. Compress and cool positrons
Related physics: Plasma physics, evaporative cooling, sympathetic cooling (Be+), Laser cooling
Related equipment: Beryllium source, Beryllium ablation laser, Beryllium cooling laser -
6a. Measure plasma size or temperature or particle count
Related physics: MCP, Detectors, Faraday cup
Related equipment: MCP, Detectors, Faraday cup
(Destructive step… so start over!) -
6b. Mixing (synthesis of antihydrogen)
Related physics: Antihydrogen, Mixing
Related equipment: Atom trap -
7. Store antihydrogen
Related physics: Antihydrogen, loffe-pritchard trap
Related equipment: Atom trap -
8. Interact with antihydrogen
Time to perform an experiment!
Related physics: LyALPHA Laser, 243nm-Laser, Microwaves, Gravity Measurements, Charge of antihydrogen
Related equipment: LyALPHA Laser, 243nm-Laser, Microwave generator -
-
10. Release antihydrogen
Turn of the atom trap to see what's left over
Related physics: Annihilation, Detectors
Related equipment: SVC, TPC, Atom Trap
